蕨菜中的一個新高黃烷醇
陳乃東,陳乃富* ,王 濤,張 莉,陳存武
1皖西學院生物與制藥工程學院;2植物細胞安徽省工程技術研究中心,六安237012;3中國藥科大學新藥篩選中心,南京210009
Introduction
Pteridium aquilinum(L.)Kuhn(Pteridaceae)is a herbaceous perennial plant. The immature, tightly curled emerging fronds are commonly used as a vegetable.The species is traditionally used to heal jaundice with damp-heat pathogen,rheum arthritis,and hypertension[1]by the Chinese people and is broadly distributed in Eastern and Southern China.Previous phytochemical investigation of this plant has led to the isolation of a variety of proanthocyanidins[2,3],and flavonol glycosides[4-10]and homoflavonoids[11].As a partof serial investigations on Pteridaceae,and in order to seek more novel bioactive compounds,an extensive chemical study on P.aquilinum was carried out,and a novel homoflavonoid with an unprecedented homoflavonol skeletone(1)(Fig.1)together with three known flavonoids quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside(2),rutin(3)and kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside(4),was obtained from the ethyl acetate extract.To our knowledge,this is the first reported case about the rare homoflavonoid isolated from P.aquilinum.Described herein are the isolation,structural elucidation and cy-totoxic evaluation of the novel flavonoid(1).
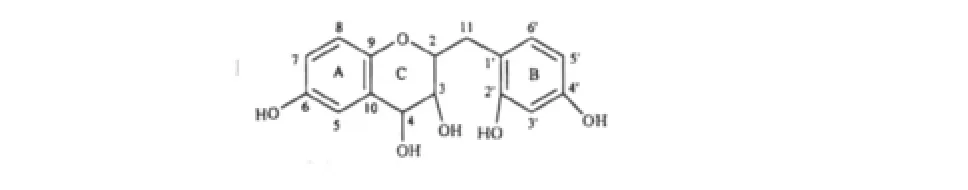
Fig.1 Chem ical structure of com pound 1
M aterials and M ethods
General
TLC was performed on silica-gel plates(Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory),with AcOEt:MeOH:H2O(20∶1∶0.5)as eluent;visualization under UV light and by spraying with AlCl3(5%in EtOH).Column chromatography(CC):silica gel(SiO2200-300;Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory).Sephadex LH-20(Sigma-Aldrich Co.,Ltd).Melting points:X4 micro melting point apparatus;Optical rotations(ORD):JASCO P-1020 polarimeter;IR Spectra:Avatar 670 FTIR spectrophotometer(Thermo Nicolet),as KBr pellets;in cm–1.EI-MS:a Bruker APEX II mass spectrometer(Bruker Daltonik GmbH,Bremen,Germany);in m/z(rel.%).1H and13C NMR Spectra:Bruker AM-400 MHz and DRX-500 MHz spectrometers,in DMSO-d6;δin ppm,J in Hz.
Plantmaterial
P.aquilinum were collected from Tiantangzhai,Anhui province,P.R.China,in July 2010 and identified by Professor Shou-biao Zhou of Anhui Normal University(specimen No.2010-07-3).
Extraction and isolation
The dried aerial parts(16.5 kg)were extracted with ethylether(50°C)to remove lipid soluble pigments.The gruffs remaining was extracted three times with 80%EtOH for 5 h under reflux.The extract was retrieved EtOH under reduced pressure to give a residue which was partitioned between petroleum ether,CHCl3,AcOEt,1-Butanol,and H2O three times successively.After evaporation,the AcOEt fraction(174 g)was chromatographed on a SiO2column gradiently eluted with AcOEt/MeOH(1∶0,40∶1,10∶1,2∶1,0∶1,v/v)and four fractions(Fr.1-4)were obtained from the part eluted by AcOEt.Fr.3(13.2 g)was submitted to Sephadex LH-20 chromatography with an eluent of MeOH/H2O to afford fractions P1-6.P2(130 mg)was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 repeatedly eluting with MeOH and further purified by recrystallization in MeOH/CHCl3(1∶1,v∶v)to yield compound 1(6 mg).AcOEt/MeOH(10∶1)fraction(32.0 g)was also repeatedly eluted with MeOH/H2O onto Sephadex LH-20 column and further purified by recrystallization in MeOH to yield compound 2(25 mg),3(100 mg)and 4(45 mg).
Cytotoxicity assay
Six human cancer cells linesweremaintained in RPMI-1640 medium.The cellswere cultured in Nunc disposable 384-well plates containing 45μL of growth medium per well and were incubated at 37℃in a humidified incubator with 5%CO2.5 μL of samples were added to the cultures at24 h of incubation.After 72 h of incubation with the samples,5 μL of Prestoblue(5 mg/mL)were added to each of the wells.The optical density wasmeasured using a Freedom EVOlyzer(TECAN,Switzerland)at 560 nm with reference wavelength at590 nm.In all experiments,three replicates were used.Adriamycin was used as positive control.
Results and Discussion
Structural identification
Compound 1,yellow power,mp 172-173 ℃;[α]=+17°(c=0.05,MeOH);IR(KBr)νmax3325,1752,1721,1510,1014,1198,935 cm-1;Itsmolecular formula,C16H16O6,was established on the basis of HR-ESI-MS for the[M+H]+ion atm/z305.1036(calculated:305.1025).The1H NMR spectrum of 1(Table 1)showed six aromatic resonances atδH7.47(d,J=4.0 Hz,1H),7.04(d,J=2.0 Hz,1H),6.23(d,J=6.0 Hz,1H),7.01(dd,J=1.5,8.0 Hz,1H),6.76(d,J=8.0 Hz,1H),and 6.68(s,1H).The1H NMR spectrum of1 also indicated the presence of three aromatic hydroxyl groups atδH12.44,9.61,9.13 and two chelated hydroxyl groups atδH4.99,4.99.
The13C and DEPT NMR spectra(Table 1)revealed the presence of one methylene,ninemethines(including three oxygenated alkane carbons δc69.8,67.7,65.4)and six quaternary carbons(involving three hydroxylated aromatic carbons δc145.5,148.4 and 166.0).The structure of 1 was suspected to be a flavanol on the basis of above-mentioned data.
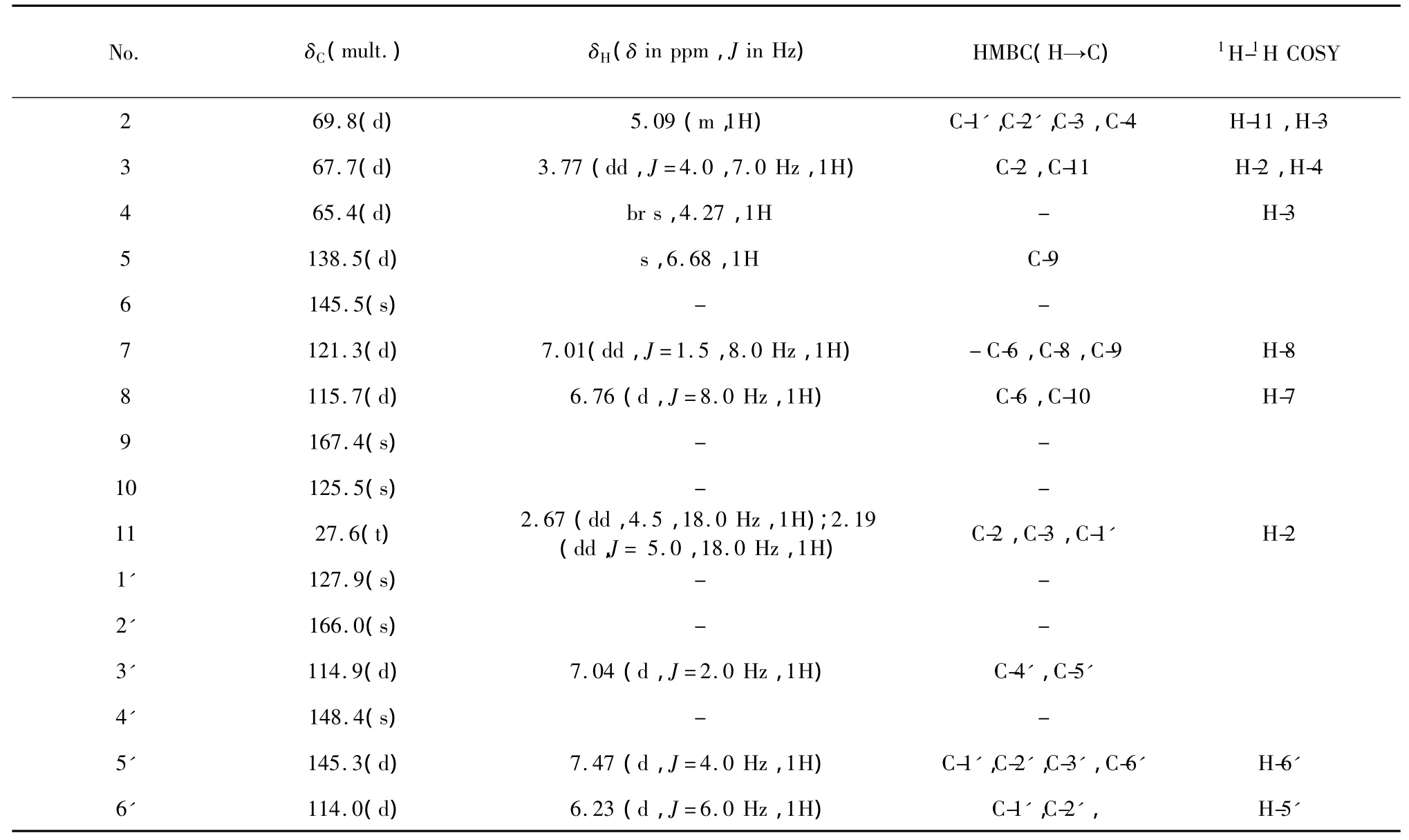
Table 1 The 1 H NMR(500 MHz),13 C NMR(125 MHz)data,HMBC and 1 H-1 H COSY correlations of com pound 1 in DM SO-d6
The gross structure of 1 was elucidated by analysis of1H-1H COSY and HMBC spectra data in DMSO-d6.The1H-1H COSY spectra of 1 revealed connectivities of three partial structures:a(δH2.67/2.19-δH5.09-δH3.77-δH4.27),b(δH7.01-δH6.76),c(δH6.23-δH7.47)as shown in Fig.2.The HMBC cross-peaks of δH7.01 to δc145.5 and δc167.4,δH6.76 to δc125.5,and δH6.68(the H of δc138.5 according to HSQC spectrum)showed HMBC correlations to δc167.4(Table 1),suggested fragment b(δH7.01-δH6.76,assigned H-7,H-8),δc145.5(assigned C-5),δc138.5(assigned C-6), δc167.4(assigned C-9)and δc125.5(assigned C-10)(Fig.2,Table 1)might be in a ring(A ring of 1).The factδH7.47 exhibited HMBC correlations to δc127.9,δc166.0 and δc114.9,and δH7.04(the H ofδc114.9)showed HMBC correlations to δc148.4 and δc145.3,disclosed that fragment c(δH7.47-δH6.23,assigned H-5',H-6')and δc127.9(assigned C-1'),δc166.0(assigned C-2'),δc114.9(assigned C-3')and δc148.4(assigned C-4')in a ring(B ring of 1).As for fragment a(δH2.67/2.19-δH5.09-δH3.77-δH4.27),the HMBC correlations ofδH2.67/2.19 and δH5.09 to C-1'indicated thatδH5.09,δH3.77,δH4.27(Fig.2,Table 1)were the signals of the H of C ring(H-2,H-3,H-4)and B ring was confirmed to connect with C ring via C-11.Thus,a homoflavanol skeleton was confirmed in 1.
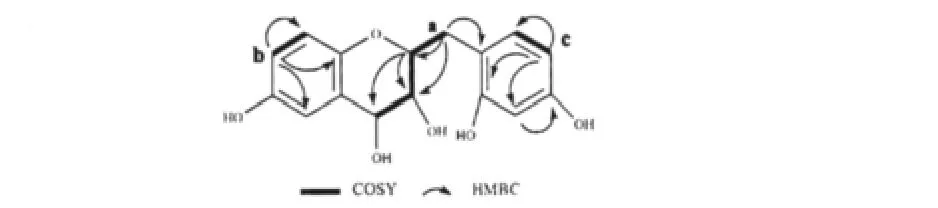
Fig.2 The key 1 H,1 H-COSY and HMBC correlations of compound 1 in DMSO
The three aromatic hydroxyl groups were assigned by the analysis of NOESY spectrum.The NOESY correlations ofδH9.61 and δH9.13(Fig.3),considering the HMBC and1H-1H cosy analysis,revealed the two aromatic hydroxyl groups were meta HO-of C ring of 1(assigned HO-C2'and HO-C4',respectively),and the aromatic hydroxyl group δH12.44 was HO-of A ring(assigned HO-C6).The H-2 showed NOESY correlations to H-3 while no crosspeakswere observed be-tween H-2 and H-4,H-3 and H-4.This suggested that the C-H chemical bonds at C-2 and C-3 were equatorial while axial bonds for the C-H at C-3 and C-4.Therefore,the configuration of H-2 and H-3,H-3 and C-4 were cis-and trans-, respectively. Thus, the structure of 1 was elucidated as 3,4,6,2',4'-penta hydroxyl-2,3-cis-homoflavan-3,4-trans-diol,a novel homoflavonoid with an unprecedented homoflavanol skeleton.
Compounds 2-4 were identified by comparisons of their spectral data with the literature values as quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside[12](2),which was first isolated from P.aquilinum,rutin[13](3)and kaempferol3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside[14](4),which had ever been isolated from this plant by F.Imperato[10]and T.Nakabayshi[15],respectively.
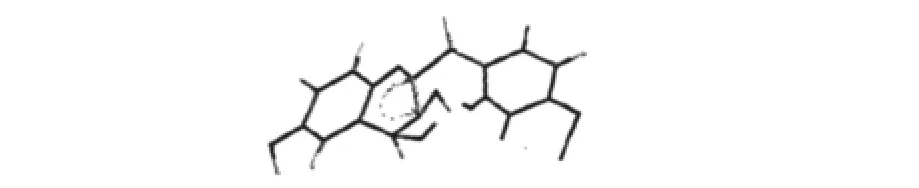
Fig.3 Selected NOESY correlations and relative stereochem istry of com pound 1
Cytotoxic activities
The primary antitumor activities of compound 1-4 against six cancer cells were evaluated(Table 2).1 showed potent cytotoxic activities to melanoma cell A375(IC50=6.2 μM),glioma U-7MG(IC50=15.5 μM)and BEL-7402(IC50=38.4 μM)while no cytotoxic activities to hepatoma carcinoma cell BEL-7402,gastric carcinoma SGC-7901 and prostatic carcinoma PC-3 were observed in our experiments.The further investigations are undertaking.
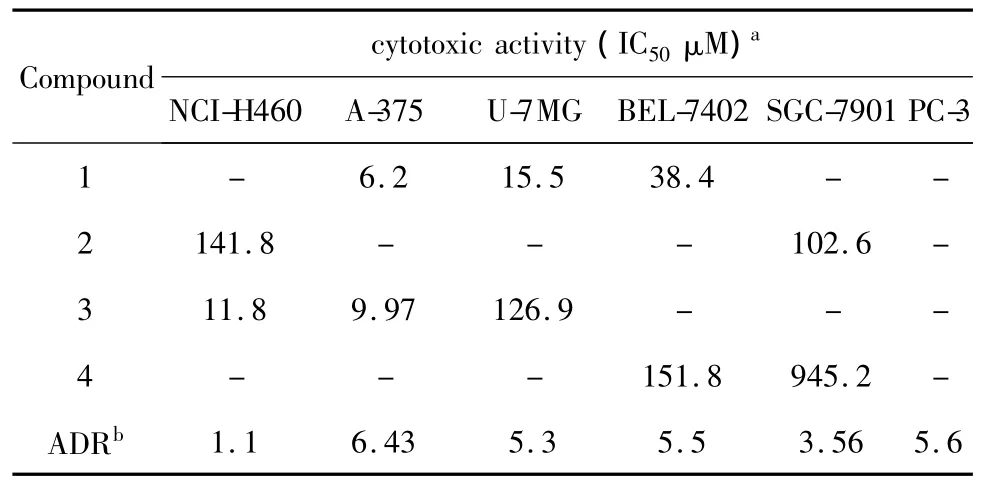
Table 1 In vitro cytotoxic activities of com pound 1-4
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province(No.090413113),the Provincial-Level Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Education Department(KJ2009A165, KJ20108259,KJ2012A277),National Natural Science Foundation of China(NSFC No.81274021)and the Research Project of Lu’an City(2011LWA001).The authors thank Dr.Dong-Jun Chen,analyzing and Testing Center of China Pharmaceutical University,for measurements of ESI-MS,NMR.The authors also thank Dr.Tao Wang,the National Drug Screening Center of China Pharmaceutical University,for detection of the cytotoxic activity of the compounds reported in the paper.
1 Zhao SX,Huang TK,Ding ZZ.Tzu Haiof Traditional Chinese Medicine(III).Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Press,1997.
2 Markham KR.The Flavonoids Advances in Research Since 1980.London:Hapman and Hall,1988.83-84.
3 Voirin B.Recherches chimiques,taxinomiques et physiologiques sur les flavonoids des pteridophytes.France:University of Lyon,PhD,1970.
4 Imperato F.Kaempferol 3-O-(5"-feruloylapioside)from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1996,43:1421-1423.
5 Imperato F.Kaempferol 7-O-rhamnoside-4-O-glucoside from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1998,47:911-913.
6 Wang CY,Mahir PA,Bryan GT.Isolation of fumaric acid,succinic acid,astragalin isoquercitrin and tiliroside from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1973,12:2298-2299.
7 Cooper GA.Chernotaxonomy and phytochemical ecology of bracken.Botan J Linn Soc,1976,73:35-46.
8 Imperato F.Rhamnetin 3-O-laminaribioside from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1997,45:1729-1730.
9 Imperato F,Minutiello P.Kaempferol-3-O-(6-O-caffeoylgluco-side)from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1997,45:199-200.
10 Imperato F.Flavonol glycosides from Pteridium aquilinum.Phytochem,1995,40:1801-1802.
11 Chen ND,Chen NF,Chen CW,etal.Separation and structure elucidation of a new homoflavanol derivative from Pteridium aquilinum(L.)Kuhn.Nat Prod Res,2013,Accepted.
12 Liu H,Mou Y,Zhao JL,et al.Flavonoids from Halostachys caspica and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities.Molecules,2010,15:7933-7945.
13 Markham KR,Geiger H.The Flavonoids Advances in Research since 1986.London:Chapman & Hall,1994.
14 Thirugnanasamambantham P,Viswanthan S,Reddy K,et al.Analgesic activity of certain bioflavonoids.Indian J Pharm Sci,1985,47:230-231.
15 Nakabayshi T.Isolation of astragalin and isoquercitrin from bracken,Pteridium aquilinum.Bull Agric Chem Soc Jpn,1955,19:104-109.