Dispersion Relations of Sound in Air and Their Properties at Low Frequency and VHF
M IN-Q i,ZhANG Q ing-You(Depar tment of Physics,Hong he University,Mengzi 661100,China)
Dispersion Relations of Sound in Air and Their Properties at Low Frequency and VHF
M IN-Q i,ZhANG Q ing-You(Depar tment of Physics,Hong he University,Mengzi 661100,China)
Some dispersion relations are derived directly from governing equations of sound in air.The properties of the dispersion relations at low frequency and VHF are investigated respectively through s implification.
governing equations;dispersion relation;dispersion;attenuation
I Introduction
It iswell known that sound can exist only in the presence of elastic medium.Unfortunately,except idealmedium,all actualmedia absorb sound energy due to viscosity,conductivity and relaxation process induced in the propagation of sound.Such absorption phenomenon is called in common attenuation or dissipation of sound.Attenuation generally varies with the difference of sound frequency.Dispersion is the other interesting phenomenon apart from attenuation in the propagation of sound.Namely,velocity of sound varies with frequency as the analog of light in rainbow in optics.Neither attenuation nor dispersion evolves by itself.They are connected quantitatively by dispersion relation rooted in causality of deep philosophical significance[1].There are many forms of dispersion relations according to differentmethods available in current literatures,but none is directly derived by governing equations that medium satisfies[2-4].Taking air as example,the paper is intended to cast light upon the direct derivation of dispersion relation with governing equations.Further more,the paper investigates the properties of the dispersion relations of air at both low frequency and VHF respectively by simplifying the derived dispersion relations.These properties include adiabatic propagation characteristic at low frequency and attenuation dropping down atVHF.
IID ispersion relation
Technologically,sound propagation is a nonlinear physical process.Nevertheless,the process can be well described with linear mathematical model under the condition of s mall amplitude.Most of all,there is no hypostatic difference be tween linear and nonlinear model to derive dispersion relation.To demonstrate the direct derivation concisely,the following discussion is confined to linear range,and meanwhile to one dimension Euclidian coordinate(1-D).
A.Governing equations
Gas disturbed by sound satisfies the following governing equations formotion,continuity,energy and state[5].In 1-D,the motion equation is
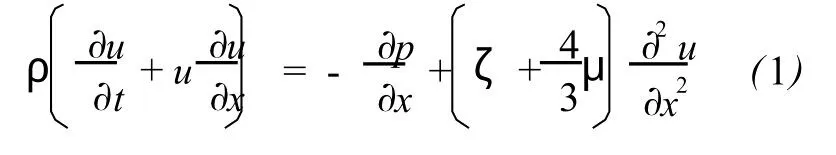
where x is the coordinate along sound propagation,ρ,рand u are the density,pressure and particle velocity of air,respectively.It iswell known they are often used to prescribe the state of gas.μis the viscosity coefficient of air andζthe second viscosity coefficient,they are one of the main reasons for the attenuation of sound.The continuity equation takes the for m
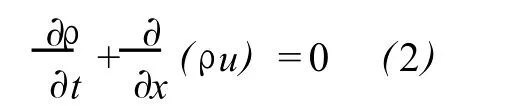
and the energy equation is written as
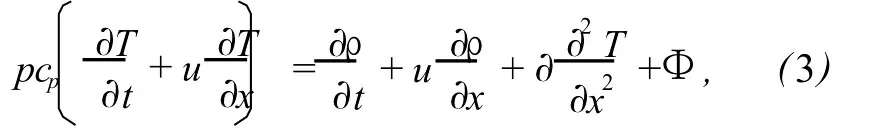
cpis the isobaric heat capacity andκis the thermal conductivity whose value decides how much energy of sound is dissipated by heat conduction.As a result,κis the other of the main reasons of attenuation.фis the attenuation function and can be ignored when the energy equation is linearized.The setof governing equations is closed by assuming the state equation of perfect gas is valid to air,namely,
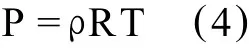
R is the universal constant of perfect gas.
B.L inearization
The set of governing equations that consist of equations(1)-(4)iswidely used in acoustics.Here,only their linear sides are exploited.At rest,the air is at static pressure p0,ρ0density and temperature T0.Being disturbed,the air stays as
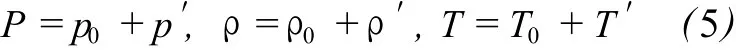
where the prime means perturbation.In comparison with static value p0,ρ0and T0,the perturbation p′andρ′are supposed to be s mall enough to satisfy the requirement of linearization.Substituting(5)and u=u’into the governing equations(1)-(4)readily leads to
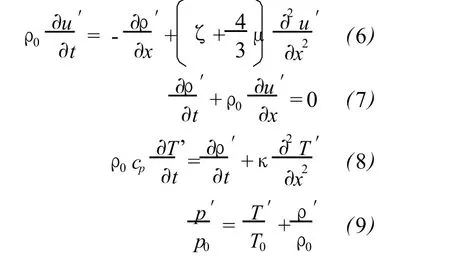
Equations(6)-(9)are the linearized governing equations.Let perturbation to be
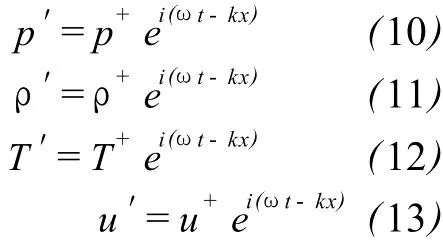
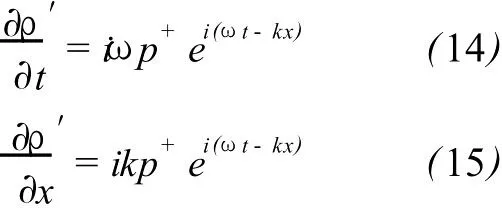
Based upon(10)to(15),a set of algebraic equation is obtained:
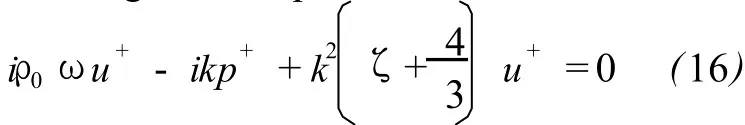
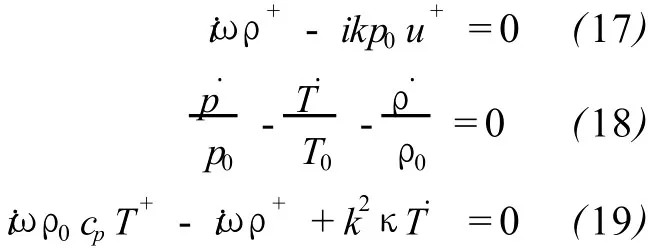
There are four unknown variables p+,ρ+,T+and u+in the four equations(16)-(19),the equation set is closed and solvable.
C.Solution
The equation set(16)-(19)is algebraic and closed.So,the solution of its can be built on algebraic theory.(16)-(19)can be rewritten with matrix as
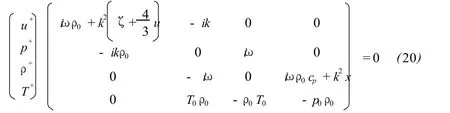
According to Cramer’s rule,the coefficient determinant(20)should be equal to zero if the variables p+,ρ+,T+and u+want to have non-zero solution at same time.Namely,
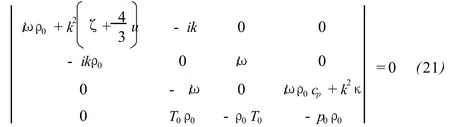
Then,the following dispersion relation of air can be obtained[6]:
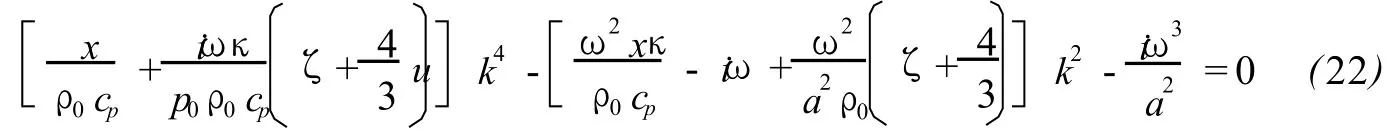
III Properties of dispersion relation
The dispersion relation(22)is a four-order algebraic equation of wave numberκ,which not only links upκ and physical parameterκ,ζandμmathematically but also builds up a kind of dependence of velocity on attenuation of sound physically,unlike the relaxation theory only deals with the relationship between attenuation and frequency.Nevertheless,(22)is too tangled to find out any of simple analytic expressions.As such,an expression ofκis worked out first and then the expression is simplified and investigated at both low frequency and VHF.
A.The expression ofκ
In order to work out the expression ofκ,let
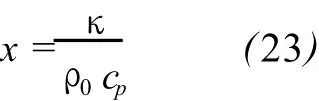
x is called the rm al diffusivity,and
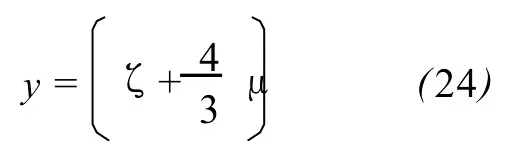
Then,the dispersion relation(22)is deformed as
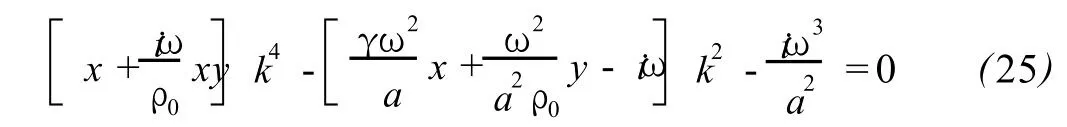
An expression ofκisworked out
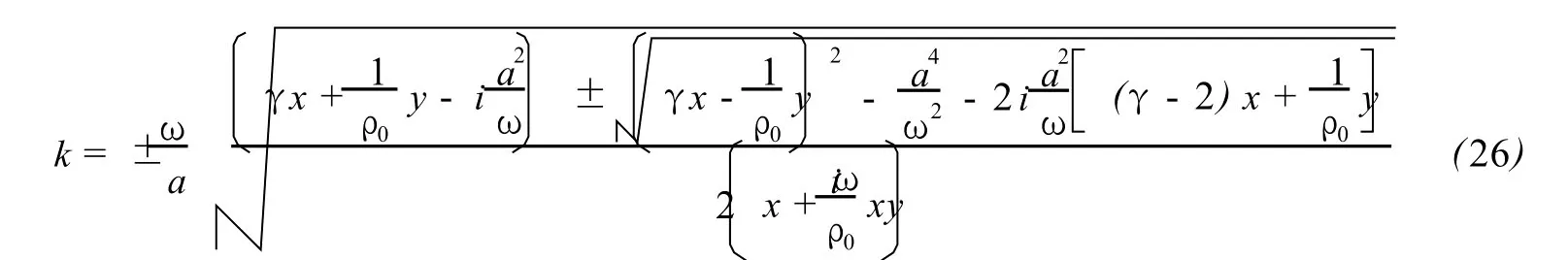
According to(10)-(13),wave numberκis complex number and can be taken as
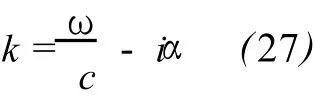
where c is the actual velocity of sound in air.(27)makes clear that the real part ofκis a function of frequency ω,and meanwhile the imaginary part represents attenuation.According to(27),the dispersion as well as the dependence of velocity upon attenuation in(26)becomesmore obvious than in(22).Even so,(26)is still entangled.
B.Low frequency
The second viscosity coefficientζis complicated because it is related to the molecule relaxation process that is the reason of anomalous absorption of sound,and moreover the characteristic spectrum of anomalous absorption is different under different condition.Fortunately,the anomalous absorption of air only take splace in ultrasonic.The thermal diffusivityχis generallymuch less than the viscosity coefficientμquantitatively.For dry air under no rmal condition,χ equals 2.22×10-5㎡/s andμ8.90×10-4㎏/m.s.In terms of dry air under no rmal conditions,the relaxation process does not work at low frequency withω<100Hz.As such,(26)can be further simplified like
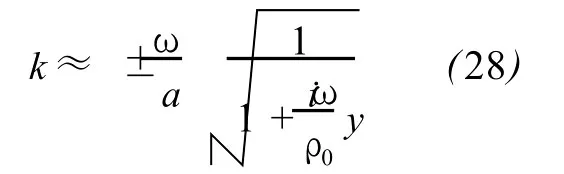
Basing on physical requirement,(28)has only an analytic expression satisfying actual requirement.That is
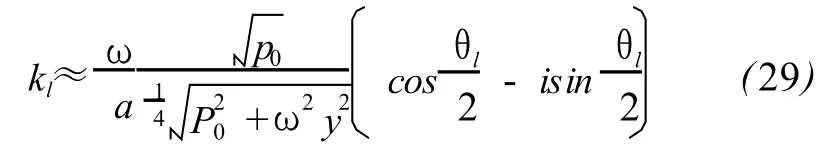
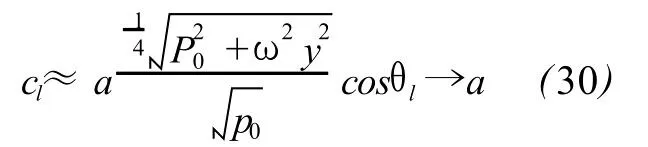
and the attenuation
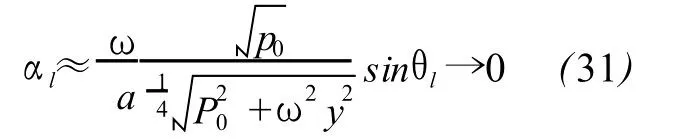
The frequency derivatives of real and imaginary part of klare
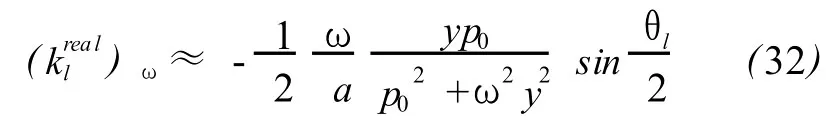
and
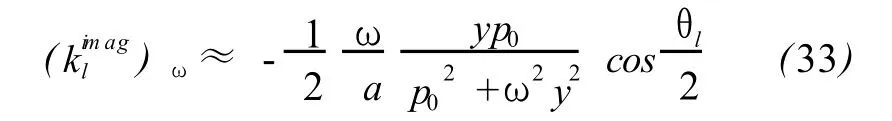
According to(30)-(33),at low frequency,the difference of ciand aswell as the attenuation coefficientαiis very small for dry air under no rmal conditions,and meanwhile ciandαiincrease very slowly with frequency.These properties supply a theoretical explanation to the inherent characteristics of infrasonic such as low dispersion and low attenuation.The thermal conduction can be ignored here since there is no thermal diffusivity x in(31)and more importantly,the upper limit of frequency can rise from 100Hz to even higher order ofmagnitude to get(28)-(33)till anomalous absorption appears,which offers a theoretical support for the adiabatic propagation assumption of sound that is a base of acoustics.
C VHF
The frequency above 100MHz is called VHF.The relaxation process happensmainly below VHF formost of gas,especially for dry air under no rmal condition.As a result,the second viscosity coefficientζseldom comes into play above VHF,and the following approximate expression withoutζcan be deduced safely by(26)
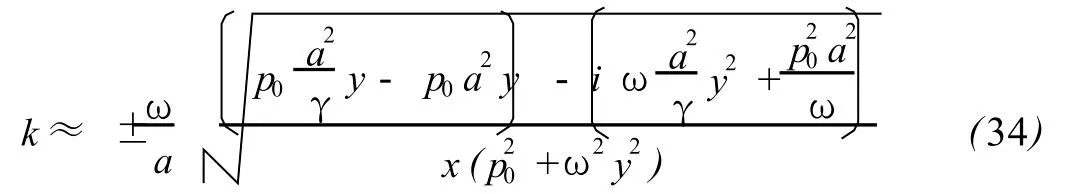
Basing upon(33),an approximate expression thatmeets physical requirement can be obtained
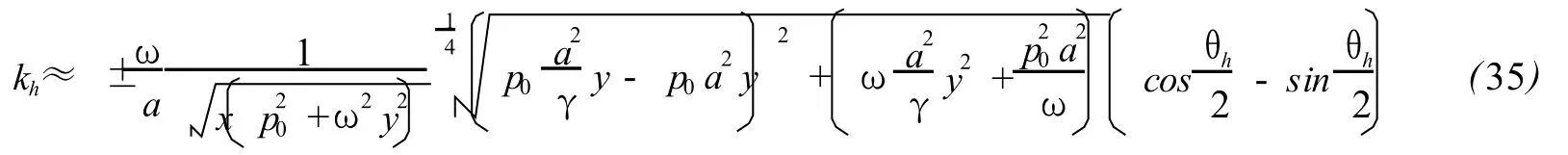
where
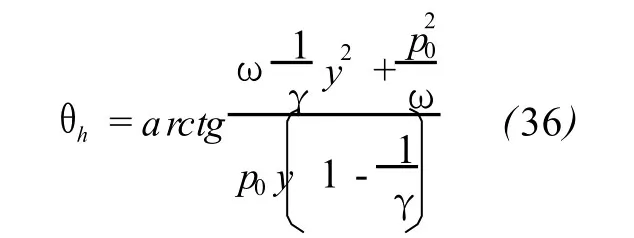
Unlike at low frequency,there exists the thermal diffusivity x in the dispersion relation(35).The derivative of the imaginary part of khversus frequency is
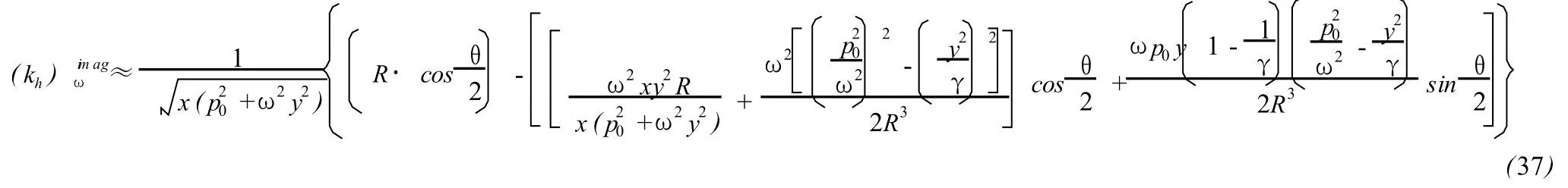
where
Acknowledgements
The first author thanksDr.Peng-Feng for constructive suggestions.The work is financially supported by Provincial Department of Education of Yunnan under the research project No.5Y0040A and Hong he University under the research project No.XJ IY0514.
[1]J.S.Toll.Causality and the Dispersion Relations:Logical Foundations[J].Phys.Rev.,1956,104(6).
[2]Adam Q.Bauer,etc.Is the Kramers-Kronig Relationship Between Ultrasonic Attenuation and Dispersion Maintained in the Presence of Apparent Losses due to Phase Cancellation[J].JASA,2007,122(1).
[3]W.Chen and S.Ho lm.Modified Szabo’sWave Equation Models for Lossy Media Obeying Frequency Power Law[J].JASA,2003,114(5)4.
[4]JanuszWojcik.Conservation of Energy and Absorption in Acoustic Fields for Linear and Nonlinear Propagation[J].JASA,1998,104(5).
[5]L.D.Landau,E.M.Lifshitz.Fluid Mechanic[M].Beijing World Publishing Co.,1995:251–308.
[6]F.HughesW illiam,John A.Brighton.Fluid Dynamics[M].Academic Press,Beijing,2002:67–295.
[7]L.L.Beranek.Acoustic Measurement[M].JohnW iley&Sons,1988:37–83.
[8]Allan J.Zuckerwar,RogerW.Meredith.Low-frequency Absorption of Sound in Air[J].JASA,1985,78(3):946–955.
[9]G.P.Howell,C.L.Morfey.Frequence Dependence of the Speed of sound in Air[J].JASA,1987,82(1):375–376.
[10]George S.K.Wong.Speed of Sound in Standard Air[J].JASA,1986,79(5):1359–1366.
[11]P.M.Morse.Vibration and Sound[M].McGraw-Hill,1936.
[12]Lord Rayleigh.Theory of Sound[M].London,1929.
[13]JohnW.Dooley,Measurement of Small Changes in Sound Velocity in the UHF Range[J].JASA,1970,47(5):1232–1235.
[14]H.E.Bass and F.Douglas Shields.Absorption of Sound in Air:High Frequency Measurements[J].JASA,1977,62(3).
[15]Karl F.Herzfeld.Absorption and Dispersion of Ultrasonic Waves[M].Academic Press,1959.
[16]C.Ener.A.F.Gabrysh and J.C.Hubbard.Ultrasonic Velocity,Dispersion,and Absorption in Dry,-free Air[J].JASA,1952,24(5).
[17]Flond Dunn and John E.Breyer.Generation and Detection of Ultra High Frequency Sound in Liquids[J].JASA,1962,34(6).
2010-03-26
閔琦(1972-),男,云南人,中科院聲學所在讀博士,副教授。研究方向:聲學及理論物理。
O 441
A
1008-9128(2010)02-0010-06
[責任編輯 姜仁達]

