化學鍍鎳槽熱損失的最小化
// SRINIVASAN K N, SELVAGANAPATHY T, MEENAKSHI R, JOHN S
摘 要:在不使用電能的情況下,化學鍍依靠含有還原劑的水溶液中金屬離子的催化還原,從而實現金屬的沉積。其成功與否,很大程度上取決于溫度的維護。溫度升高,沉積速度加快,因此,應當避免熱量散失到周圍環(huán)境中。本文估算了包裹不同隔熱材料的化學鍍鎳液的散熱量。結果表明,采用棉花作為隔熱材料,熱損失可降至最低,從而提高并維持一定的沉積速率。
關鍵詞:鎳磷合金;化學鍍;熱損失;隔熱材料
Electroless nickel is usually considered as an engineering coating due to its excellent corrosion and wear resistance, good ductility, lubricity, and solderability,
化學鍍鎳槽熱損失的最小化
// SRINIVASAN K N, SELVAGANAPATHY T, MEENAKSHI R, JOHN S
摘 要:在不使用電能的情況下,化學鍍依靠含有還原劑的水溶液中金屬離子的催化還原,從而實現金屬的沉積。其成功與否,很大程度上取決于溫度的維護。溫度升高,沉積速度加快,因此,應當避免熱量散失到周圍環(huán)境中。本文估算了包裹不同隔熱材料的化學鍍鎳液的散熱量。結果表明,采用棉花作為隔熱材料,熱損失可降至最低,從而提高并維持一定的沉積速率。
關鍵詞:鎳磷合金;化學鍍;熱損失;隔熱材料
1 Introduction
Electroless nickel is usually considered as an engineering coating due to its excellent corrosion and wear resistance, good ductility, lubricity, and solderability,
excellent electrical properties and high hardness[1-5]. The concentration of bath constituents, pH, temperature, and agitation are the factors which affect the rate of deposition, the nature of deposit and the phosphorous content of the deposit[6-8]. The deposition rate is proportional to the bath temperature and hence, in electroless plating, the bath is heated to a high temperature to take advantage of high deposition rate obtained[2-3,9-11]. Bath temperature also influences the uniformity and composition, hence the mechanical properties of the electroless deposit[2-3]. But, heat loss may take place through the concrete floor, the vertical surfaces of the tank wall, or from the surface of the electrolyte. Hence, it is necessary to minimize the heat loss from electroless plating bath. The present work aims to study the amount of heat lost from the electroless bath and its minimization.
2 Experimental
2. 1 Estimation of heat loss
The plating tank is made of polypropylene material. The dimension of the tank is: Length = 30 cm, Breadth = 30 cm, Height = 25 cm, and Holding capacity = 25 L.
The bottom of the plating tank is rested in concrete. The side walls are exposed to the ambient conditions. The plating tank is operated at a temperature of 90 °C and maintained by thermal relay control system. The surrounding room temperature is about 35 °C. Hence there exists a very large temperature difference. So heat is continuously lost to the surroundings, through the walls of the tank. Heat is lost by conduction, convection, radiation and evaporation. For example, in the case of evaporation, loss of water from the bath may change the concentration of bath constituents and it may result in a consequent change in the deposition rate. Hence, there is a need for an improved electroless plating process with minimum heat loss, which can provide high quality and uniform deposits with excellent properties.
To minimize heat losses through the walls of the tank, the tank walls are lined with suitable substances of low thermal conductivity. This will result in the prevention of heat losses and hence for power conservation and better power utilization. Hence, heat loss from the electroless bath was estimated before and after insulation. The materials selected for insulation are expanded polystyrene, glass wool, cotton, sand, saw dust and rice straw. The thickness of the insulating materials employed was constant (25 cm). Also, the time taken for both heating the electroless bath to 90 °C and the heat loss up to room temperature with insulation was noted every half an hour.
2. 2 Sample preparation and characterization
Mild steel panels (15 cm × 10 cm) were subjected to acid dip initially and cleaned with washing powder to obtain a wet surface, and then dried using an air drier. The weight of the panel was determined using an electronic balance. The panels were rinsed with distilled water and subjected to plating in the electroless bath. The weight of the panel after electroless plating was determined. From the difference in the two weights, the coating thickness was calculated.
The optimized bath composition and operating conditions for electroless Ni–P plating is as follows:
Nickel sulfate 25 g/L
Sodium hypophosphite 20 g/L
Trisodium citrate 50 g/L
Stabilizer 1-2 ppm
pH 7.0-7.5
Temperature 90 °C
The bath was subjected to mechanical agitation at a rate of 300 r/min. The constituents of the bath, nickel sulfate and sodium hypophosphite, were properly replenished depending upon the residual nickel content in the bath. The nickel content was analyzed by EDTA complexometric titration. Sodium hypophosphite was analyzed by iodometric titration. The pH of the solution was controlled by suitable addition of 1:1 ammonia.
3 Results and discussion
The amount of heat lost from the electroless bath was calculated by the following methods.
(a) Heat loss by conduction:
The mathematical expression for the rate of heat transfer due to conduction is,
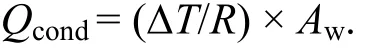
Where
?T = Temperature difference between electrolyte and the tank wall in °C,
R = Resistance of the material in m2·K/W,
Aw= Area of the heat transfer in m2.
(b) Heat loss by convection:
The mathematical expression for the rate of heat transfer due to convection is,
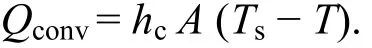
Where
hc= Convective heat transfer coefficient in W/(m2·K),
A = Area of heat transfer in m2,
Ts= Surface temperature in °C,
Tf= Fluid/gas temperature in °C.
(c) Heat loss by radiation:
The rate of heat transfer can be calculated by the given mathematical expression,
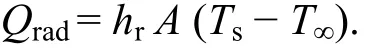
For easier comparison with the convective heat rate, the heat radiation coefficient can be defined as

Where
εs= Surface emissivity,
σ = Stefan Boltzmann constant = 5.67 × 10?8W/(m2·K4),
A = Area of the tank wall in m2,
Ts= Surface temperature of the fluid in °C,
T∞= Environment temperature in °C.
(d) Heat loss by evaporation:
This can be determined using the following equation.
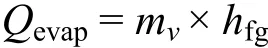
Where
mv= Mass of the liquid evaporated in kg/s,
hfg= Heat of evaporation in kJ/kg.
The amount of heat loss calculated using the above equations is given in Table 1. Further studies were carried out by heat loss due to conduction.

Table 1 Amount of heat lost from the plating tank表1 鍍槽散熱量
To minimize the heat loss, various insulating materials were used. Among the various insulating materials, minimum heat loss was observed in the case of cotton and expanded polystyrene as can be seen from the Table 2.
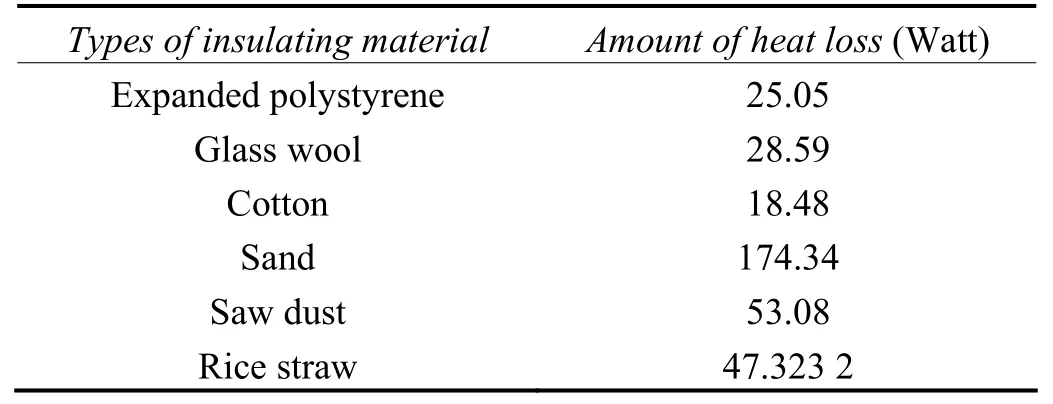
Table 2 Amount of heat lost from insulated tank表2 隔熱后鍍槽的散熱量
The increase in the temperature of the bath up to 90 °C after insulation was noted every half an hour. And then the plating tank was closed with a lid and the heat loss was noted every half an hour as given in Table 3.

Table 3 Time taken for heating and cooling to a specific temperature表3 加熱和冷卻到特定溫度所需要的時間
It was found that the heat loss was minimized when cotton was used as the insulating material. Hence cotton was selected as an insulating material for the tank for further studies. The electroless plating tank insulated with cotton is as given in Figure 1. A good rate of deposition of 16-17 μm/h was obtained and maintained when cotton was used as the insulating material.
4 Conclusion
The amount of heat lost from the electroless bath and its minimization was determined. The results can be concluded as follows:

Figure 1 Electroless plating tank insulated with cotton圖1 采用棉花進行隔熱的化學鍍槽
(1) The amount of heat loss was calculated and conduction was employed as the optimized mode of heat transfer.
(2) Among the various insulating materials used, minimum heat loss was obtained when copper or expanded polystyrene was used as the insulating material.
(3) After insulation with cotton, the time taken for heating the electroless bath to 90 °C and then cooling to room temperature was well maximized.
(4) A good rate of deposition of about 16-17 μm/h was obtained and maintained when cotton was used as the insulating material.
[1] BRENNER A, RIDDELL G E. Nickel plating on steel by chemical reduction [J]. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, 1946, 37 (1): 31-34.
[2] RIEDEL W. Electroless Nickel Plating [M]. Metals Park: ASM International, 1991.
[3] MALLORY G O, HAJDU J B. Electroless Plating: Fundamentals and Applications [M]. Orlando: American Electroplaters and Surface Finishers Society, 1990.
[4] BAUDRAND D W. Electroless Nickel Plating [M] // REIDBACH F. ASM Handbook Vol. 5: Surface Engineering. Metals Park: ASM International, 1994: 290-310.
[5] GAWRILOV G G. Chemical (Electroless) Nickel Plating [M]. Surrey: Portcullis Press Ltd, 1979.
[6] ALY I H M, YOUNAN M M, NAGEEB M T. Autocatalytic (electroless) deposition of ternary nickel-cobalt-phosphorus alloy [J]. Metal Finishing, 2003, 101 (4): 37-42.
[7] SANKARA NARAYANAN T S N, SELVAKUMAR S, STEPHEN A. Electroless Ni–Co–P ternary alloy deposits: Preparation and characteristics [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 172 (2/3): 298-307.
[8] DERVOS C T, NOVAKOVIC J, VASSILIOU P. Vacuum heat treatment of electroless Ni–B coatings [J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58 (5): 619-623.
[9] SANKARA NARAYANAN T S N, SESHADRI S K. Formation and characterization of borohydride reduced electroless nickel deposits [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 365 (1/2): 197-205.
[10] ANIK M, K?RPE E, ?EN E. Effect of coating bath composition on the properties of electroless nickel-boron films [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2008, 202 (9): 1718-1727.
[11] ORAON B, MAJUMDAR G, GHOSH B. Parametric optimization and prediction of electroless Ni–B deposition [J]. Materials & Design, 2007, 28 (7): 2138-2147.
[ 編輯:溫靖邦 ]
Minimization of heat losses from electroless nickel bath
K. N. Srinivasan1,*, T. Selvaganapathy2, R. Meenakshi3, S. John1
( 1.Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi, Tamilnadu-630006, India; 2.Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, Tamilnadu-608002, India; 3.A.V.V.M Sri Pushpam College, Poondi, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu-613503, India )
Electroless plating depends on the catalytic reduction of a metal ion in an aqueous solution containing a reducing agent and the subsequent deposition of the metal without the use of electrical energy. Its success depends to a great degree on the maintenance of temperature. Increase in temperature increases the rate of deposition and hence the heat loss to the surroundings should be prevented. In this paper, the amount of heat lost from the electroless nickel bath with different insulating materials was estimated. It becomes evident from the results that the heat loss to the surroundings is minimized when cotton is used as insulating material and it enhances and maintains the rate of deposition.
nickel–phosphorus alloy; electroless plating; heat loss; insulating material
TQ153.12 Document code: A
1004 – 227X (2010) 07 – 0027 – 03
date:2009–10–16Revised date:2010–01–06
Dr. K. N. Srinivasan, (E-mail) k_n_srinivasan@yahoo.com。
Biography: K. N. Srinivasan (1954–) took his M.Sc. in Chemistry from Madura College, Madurai in 1977 and obtained his Ph.D from Madura Kamaraj University in 1988 in the field of zinc plating. He is now holding the position of Deputy Director in Industrial Metal Finishing Division. His field of specialization is electroplating and cathodic protection. He has earned 125 publications in reputed national and international journals.

